What is ultraviolet radiation and its use?
2022-03-09
Ultraviolet (UV) occupies the electromagnetic spectrum between X-rays and visible light. The sun emits ultraviolet rays. However, most of them are absorbed by the earth's ozone layer. Just as visible light consists of different colors in a rainbow, the ultraviolet radiation spectrum is divided into three regions, called UVA, UVB and UVC. When sunlight passes through the atmosphere. All UVC and most UVB are absorbed by ozone, water vapor, oxygen and carbon dioxide. UVA is not filtered so obviously by the atmosphere. Their biological activity and degree of penetration into the skin are different
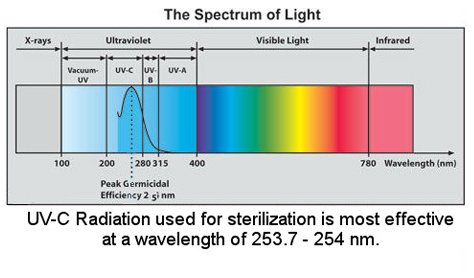
UVA wavelength:
315-400 nm. Not absorbed by the ozone layer
UVB wavelength:
280-310 nm. It is mainly absorbed by the ozone layer, but some do reach the earth's surface.
UVC wavelength:
100-280 nm. It is completely absorbed by the ozone layer and the atmosphere.
Short wave ultraviolet UVC is the most destructive type of ultraviolet radiation.
A unique feature of ultraviolet light is that its specific wavelength range, that is, the wavelength between 200-300 nm (billionth of a meter), is classified as sterilization - which means that they can inactivate microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses and protozoa. This ability makes UV widely used as an environment-friendly, chemical free and efficient way to disinfect and protect water from harmful microorganisms.
Microorganisms are simple organic structures that easily absorb UVC wavelengths, resulting in Photodegradation (destruction). Because nucleic acids are damaged, they are inactivated by ultraviolet light. The high energy associated with short wave ultraviolet energy (mainly at 254 nm) is absorbed by cellular RNA and DNA. Microbial DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the first to be adversely affected due to weak molecular bonds. In one hundredth of a second, it suffered irreparable damage. Subsequent loss of genetic instructions can lead to cell death and / or inability to replicate, making it harmless, and continuous exposure can lead to uninterrupted degradation.
UVC led refers to the way of emitting UVC. For example, mercury lamps have been used in traditional ultraviolet lamps, and mercury is very dangerous. Mercury lamps have been completely banned after Minamata convention. As a new ultraviolet sterilization method, UVC LED is the only reliable alternative today.

With the improvement of UVC led performance, the utilization rate of this relatively new technology in disinfection, life science and environmental monitoring instruments is developing rapidly. UVC LEDs can reduce footprint and power consumption, thereby increasing the cost of ownership of end users.
The spectral application of UVC LED is increasing, because they can solve the market trend of miniaturization, cost reduction and real-time measurement. It has a high utilization rate in some water sterilization, air sterilization, surface sterilization and biomedicine. The band range of UVC LED is generally 220nm-285nm.
Qingdao fluorescent Innovation Technology Co., Ltd. has a professional postdoctoral team, focusing on the research of ultraviolet sterilization application. After years of deep cultivation in the ultraviolet industry, the company has obtained a number of national invention and utility model patents. At present, a number of sterilization module products have been put into the market. For more details, please visit the company's website at www.qdyingguang.com Com contact the company for the official account of WeChat.